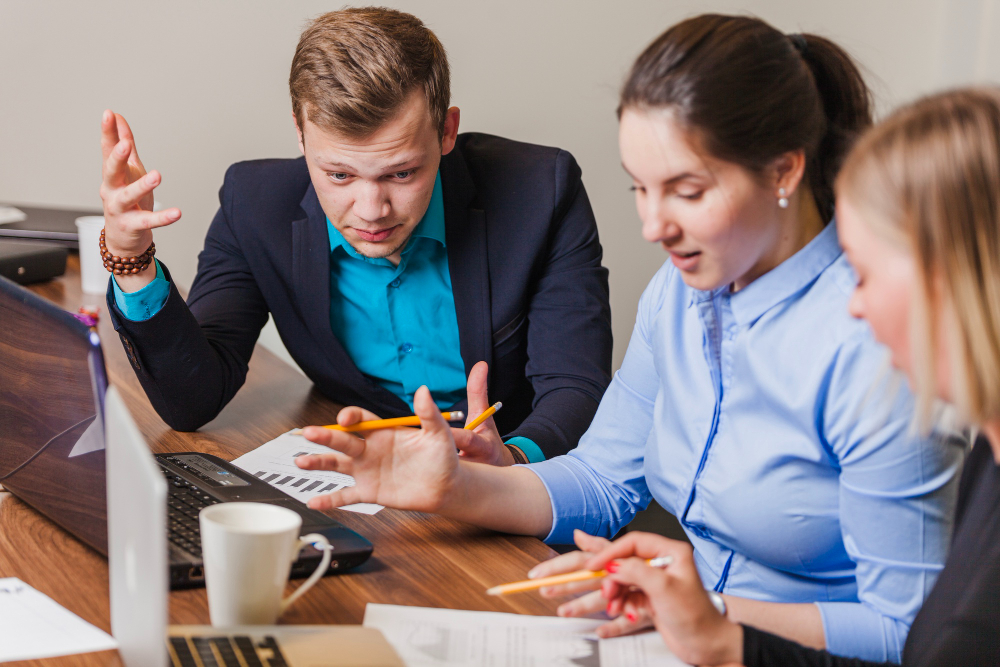
For many young companies, financial management often starts with the basics: budgeting, forecasting cash flows, and preparing simple balance sheets to satisfy reporting needs. While these tools are essential, they represent only the surface layer of what it truly means to build financial resilience. In today’s dynamic business environment—marked by technological disruption, investor expectations, and economic volatility—relying solely on traditional financial practices may leave startups underprepared for the challenges ahead.
The hidden pillars of financial flexibility stretch beyond conventional accounting. They involve cultivating the capacity to adapt rapidly, survive setbacks, and seize opportunities at exactly the right time. Young companies must think not only about how they are spending money today but also about how they can design financial systems that give them room to maneuver tomorrow. This is what differentiates a startup that simply survives from one that thrives and innovates long-term.
Financial flexibility is not just about having capital; it is about clarity, foresight, and preparedness. A startup with flexible systems can pivot when markets shift, protect itself against unforeseen risks, maintain the trust of investors, and continuously reinvest in growth without being paralyzed by uncertainty. Building such resilience goes hand in hand with cultivating a mindset that views finance not as an administrative function, but as a vital, strategic driver of competitiveness and innovation.
A truly flexible financial foundation requires intentional design. Rather than locking into rigid budgetary practices, young companies must create dynamic, living structures that grow with them. These structures should function less like static spreadsheets and more like adaptive systems—able to expand, contract, and regroup as circumstances change. Let’s explore the key elements that bring this vision to life:
1. Strategic Liquidity: More Than Just Cash on Hand
Liquidity is often simplified as keeping enough cash in the bank. But for startups, strategic liquidity is about ensuring access to capital in multiple forms and at multiple layers—emergency reserves, short-term credit facilities, and fast-turnover investments that can be liquidated if needed. By building liquidity buffers and diversifying cash reserves, startups can weather sudden expenses, unexpected downturns, or rapid surges in demand without becoming cash-strapped.
2. Smart Debt Management: Using Leverage Wisely
Debt is often viewed as a threat for young companies, but when managed intelligently, it becomes a powerful tool for growth. Smart debt management involves securing credit lines before they are urgently needed, negotiating flexible repayment terms, and using debt strategically to fuel revenue-generating initiatives rather than plugging ongoing losses. This proactive approach prevents debt from becoming a burden and ensures it supports, rather than restricts, agility.
3. Adaptive Capital Allocation: Prioritizing Growth Without Overextension
Startups frequently face the challenge of balancing aggressive growth with operational sustainability. Adaptive capital allocation means constantly reevaluating where money is invested and shifting priorities as conditions evolve. Instead of pouring every available dollar into expansion, founders should carve out funds for experimentation, continuous improvement, and resilience measures. This helps reduce overextension and gives the company room to pivot if a new opportunity emerges.
4. Investor Relations as a Two-Way Dialogue
Investor relationships should not be limited to quarterly updates or funding negotiations. Maintaining transparent, ongoing conversations with investors builds trust and strengthens long-term alignment. Especially during uncertain times, investors are more likely to offer additional support, bridge financing, or strategic guidance when they feel genuinely engaged. Treating investors as partners rather than just capital providers not only enhances financial flexibility but also expands the startup’s strategic network.
5. Scenario-Based Planning: Preparing for Multiple Futures
Perhaps the most underutilized financial tool for startups is scenario-based planning. Instead of relying on a single “best guess” forecast, founders should develop multiple financial scenarios—optimistic, conservative, and disruptive. Planning for different revenue trajectories, cost structures, and market shifts allows startups to prepare playbooks in advance. This readiness dramatically reduces the time required to respond when unexpected events unfold, giving agile companies an edge over competitors that are caught off guard.
Final Thoughts: Financial Flexibility as a Competitive Advantage
For young companies, financial flexibility is far more than a safeguard—it is a strategic advantage. In industries where opportunities appear and vanish quickly, the ability to adapt financially can mean the difference between capturing market share and missing out altogether. More importantly, financial flexibility provides the foundation for calculated risk-taking, letting startups innovate and experiment without the paralyzing fear of collapse.
By embracing strategic liquidity, leveraging debt sustainably, reallocating capital adaptively, nurturing investor partnerships, and practicing scenario-based planning, startups can build resilience into their DNA. This resilience not only safeguards survival but also empowers boldness—the ability to explore new markets, launch disruptive products, and remain competitive in environments where change is constant.
Young companies must remind themselves: financial health is not measured solely by today’s profit margins or tomorrow’s cash flow forecast. It is measured by the freedom to act, the confidence to navigate uncertainty, and the flexibility to seize the future on your own terms.